Electrochemical reduction of tungsten(VI) oxide from a eutectic melt CaCl2–NaCl under potentiostatic conditions Scientific paper
Main Article Content
Abstract
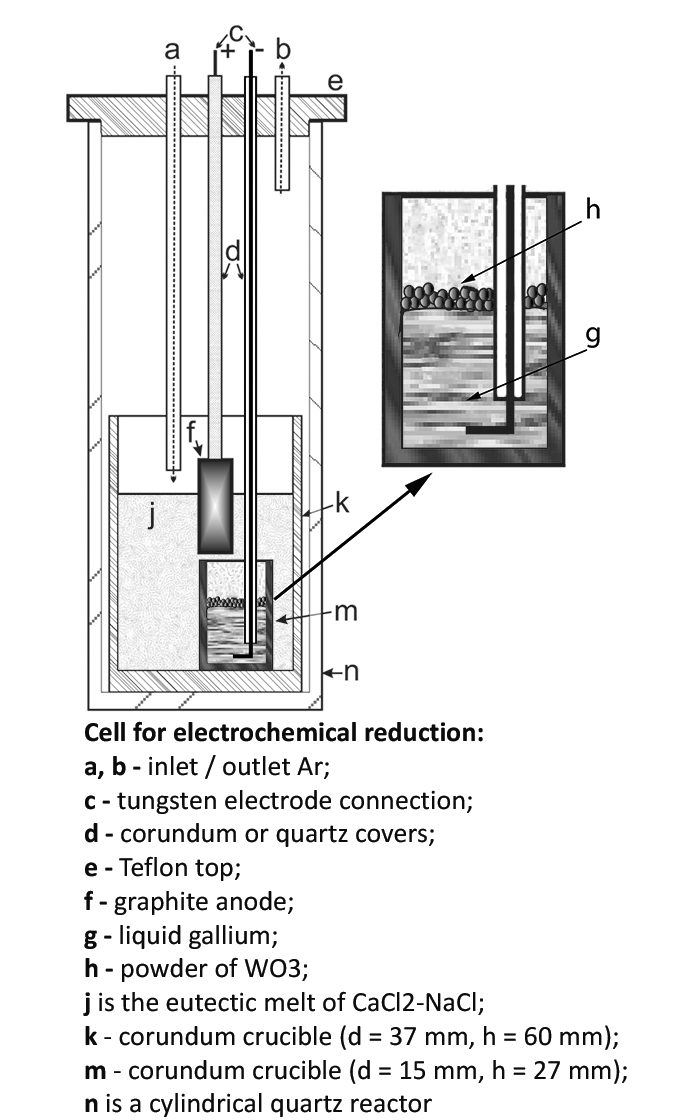
The paper presents results of the study of the electrochemical reduction of tungsten(VI) oxide in a melt of the eutectic composition 52 mol% CaCl2 and 48 mol% NaCl at a liquid gallium electrode. Scanning electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction methods were used to study the microstructures of the obtained powders. The Rietveld method which is based on diffraction patterns were used to calculate the quantitative content of phases in WO3 reduction products. The thermodynamic properties of the electrolysis process were investigated by voltammetry. It is shown that a necessary condition for the electrochemical reduction of WO3 is electrolysis at potentials higher than the standard electrode potential of decomposition of calcium tungstate, which is formed by the interaction of tungsten oxide with calcium chloride. The reduction can take place by both electrochemical and metallothermic mechanisms depending on the conditions of electrolysis. The reduction product is fine tungsten with a particle crystallite size of up to 1 μm.
Downloads
Metrics
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.

Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution license 4.0 that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
References
V. Gavrish, G. Baranov, T. Chayka, N. Derbasova, in XII International Conference Radiation-thermal Effects and Processes in Inorganic Materials, Tomsk, Russian Federation, 2016, IOP Conf. Series: Materials Science and Engineering, IOP Publishing, 2017, 012013 (http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.1088/1757-899X/168/1/012013)
E. G. Sokolov, A. V. Ozolin, S. A. Arefieva, in Materials Science Forum, Trans Tech Publications Ltd., Switzerland, 2020, p. 511 (http://dx.doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.992.511)
V. M. Gavrish, G. A. Baranov, T. V. Chayka, N. M. Derbasova, A. V. Lvov, Y. M. Matsuk, in International Scientific Conference on Radiation-Thermal Effects and Processes in Inorganic Materials, Tomsk, Russia, 2015, IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng., IOP Publishing, 2016, 012028 (http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/110/1/012028)
E. Lassner, W.-D. Schubert, Tungsten: properties, chemistry, technology of the element, alloys, and chemical compounds, Springer, Boston, MA, 1999, p. 422 (http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-4907-9)
R. Sarathi, T. K. Sindhu, S. R. Chakravarthy, A. Sharma, K. V. Nagesh, J. Alloys Compd. 475 (2009) 658 (http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2008.07.092)
U.S. Department of the Interior, U.S. Geological Survey, Metal prices in the United States through 2010: U.S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Report 2012–5188, Pubs.Usgs.Gov, Reston, VA, 2013
E. Lassner, W.-D. Schubert, E. Lüderitz, H. U. Wolf, Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, 2012 (http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14356007.a27_229)
Y. Wu, Z. Lv, H. Sun, and J. Dang, J. Mater. Res. Technol. 8 (2019) 4687 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2019.08.014)
N. E. Fouad, K. M. E. Attyia, M. I. Zaki, Powder Technol. 74 (1993) 31 (https://doi.org/10.1016/0032-5910(93)80005-U)
G. Z. Chen, D. J. Fray, in Non-Ferrous Metals Processing, TMS Light Metals, RresearchGate, Charlotte, NC, 2004, p. 881
A. M. Abdelkader, K. T. Kilby, A. Cox, D. J. Fray, Chem. Rev. 113 (2013) 2863 (https://doi.org/10.1021/cr200305x)
L. Zhang, Z. Nie, X. Xi, L. Ma, X. Xiao, M. Li, Metall. Mater. Trans., B 49 (2017) 334 (https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-017-1125-3)
J. Li, X. Y. Zhang, Y. Bin Liu, Y. G. Li, R. P. Liu, Rare Met. 32 (2013) 512. (https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-013-0156-4)
J. Li, Y. Li, L. Liu, Z. Cai, X. Zhang, R. Liu, Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 42 (2013) 2237 (https://doi.org/10.1016/s1875-5372(14)60028-x)
D. Tang, W. Xiao, H. Yin, L. Tian, D. Wang, J. Electrochem. Soc. 159 (2012) E139 (https://doi.org/10.1149/2.113206jes)
M. Erdoǧan, I. Karakaya, Metall. Mater. Trans., B 41 (2010) 798 (https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-010-9374-4)
R. Abdulaziz, L. D. Brown, D. Inman, S. Simons, P. R. Shearing, D. J. L. Brett, Electrochem. Commun. 41 (2014) 44 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2014.01.022)
T. Nohira, Т. Ide, X. Meng, Y. Norikawa, and K. Yasuda, J. Electrochem. Soc. 168 (2021) 046505 (https://doi.org/10.1149/1945-7111/abf266)
The Fact™ and FactSage™ databases, http://www.crct.polymtl.ca/fact/documentation/FS_All_PDs.htm (accessed 5.9.21)
A. P. Kreshkov, Fundamentals of Analytical Chemistry, Chemistry, Moscow, 1970, p. 472 (https://www.twirpx.com/file/379406)
H. Putz, Match! Phase Analysis using powder diffraction, Crystal impact, Bonn, 2020, p. 143 (http://www.crystalimpact.com/download/match3/Manual.pdf)
Crystallographic Computing System for Standard and Modulated Structures Jana 2006, http://jana.fzu.cz (accessed 7.9.21)
Crystallography Open Database, http://www.crystallography.net (accessed 7.9.21)
I. Barin, Thermochemical Data of Pure Substances, VCH Verlagsgesellschaft mbH, Weinheim, 1995, p. 1885 (lSBN 3-527-28745-0)
Yu. K. Delimarsky, Electrochemistry of ionic melts, Metallurgy, Moscow, 1978, pp. 223–224 (https://ua1lib.org/book/1042044/0e752b)
D. J. Fray, G. Z. Chen, T. W. Farthing, (Cambridge University), UK Patent WO 9964638, PCT/GB 99/01781 (1999).