Computer-aided approach for the identification of lead molecules as the inhibitors of cholinesterase’s and monoamine oxidases: Novel target for the treatment of Alzheimer disease Scientific paper
Main Article Content
Abstract
This article has been corrected. See JSCS 2024:89(3), doi: 10.2298/JSC240325036E
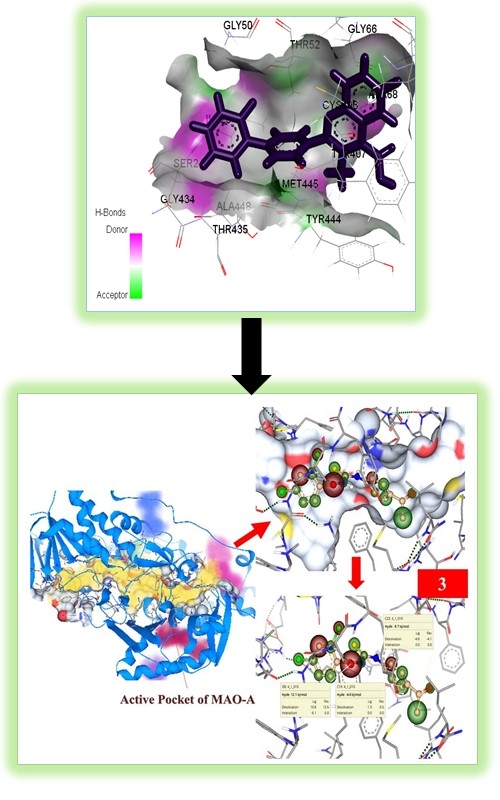
Molecular docking is a promising and reliable technology for the purpose of discovering lead compounds via virtual screening. In addition to allowing for the testing of a large number of compounds, it also allows for the determination of how the selected compounds inhibit the targeted protein/receptor based on the scoring function and ranking. Because selective cholinesterase and monoamine oxidase inhibitors play a critical role in the treatment of Alzheimer disease, this research focuses on elucidating the mechanism of binding interactions of a few quinolone derivatives within the active sites of cholinesterase (acetyl-cholinesterase (AChE) and butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) and monoamine oxidase (MAO, monoamine oxidase A & B). As a result of these discoveries, it is possible that the newly identified inhibitors will be used as lead compounds in the development of novel enzyme inhibitors for the treatment of specific diseases, hence enabling the development of novel therapeutic approaches.
Downloads
Metrics
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution license 4.0 that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
Funding data
-
King Saud University
Grant numbers RSP2024R357
References
J. M. Shine, E. J. Müller, B. Munn, J. Cabral, R. J. Moran, M. Breakspear, Nat. Neurosci. 24 (2021) 765 (https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-021-00824-6)
I. Gülçin, A. Scozzafava, C. T. Supuran, Z. Koksal, F. Turkan, S. Çetinkaya, S. H. Alwasel, J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 31 (2016) 1698 (https://doi.org/10.3109/14756366.2015.1135914)
J. Patočka, K. Kuča, D. Jun, Acta Мed. (Hradec Kral.) 47 (2004) 215 (https://actamedica.lfhk.cuni.cz/media/pdf/18059694.2018.95.pdf)
J. R. Atack, E. K. Perry, J. R. Bonham, J. M. Candy, R. H. Perry, J. Neurochem. 47 (1986) 263 (https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb02858.x)
B. Li, J. A. Stribley, A. Ticu, W. Xie, L. M. Schopfer, P. Hammond, O. J. Lockridge, J. Neurochem. 75 (2000) 1320 (https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1471-4159.2000.751320.x_)
C. N. Pope, S. Brimijoin, Biochem. Pharmacol. 153 (2018) 205 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2018.01.044
R. M. Geha, K. Chen, J. Wouters, F. Ooms, J. C. Shih, J. Biol. Chem 277 (2002) 17209 (https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110920200)
J. Grimsby, K. Chen, L. J. Wang, N. C. Lan, J. C. Shih, Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 88 (1991) 3637 (https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.88.9.3637)
R. M. Geha, I. Rebrin, K. Chen, J. C. Shih, J. Biol. Chem. 276 (2001) 9877 (https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M006972200)
J. Grimsby, N. C. Lan, R. Neve, K. Chen, J. C. Shih, J. Neurochem. 55 (1990) 1166 (https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb03121.x)
K. N. Westlund, R. M. Denney, L. M. Kochersperger, R. M. Rose, C. W. Abell, Science 230 (1985) 181 (https://doi.org/10.1126/science.3875898)
R. J. Castellani, R. K. Rolston, M. A. Smith, Disease-a-Month 56 (2010) 484 (https://dx.doi.org/10.1016%2Fj.disamonth.2010.06.001)
C. Geula, S. Darvesh, Drugs Today 40 (2004) 711 (https://doi.org/10.1358/dot.2004.40.8.850473)
M. Mesulam, A. Guillozet, P. Shaw, B. Quinn, Neurobiol. Dis. 9 (2002) 88 (https://doi.org/10.1006/nbdi.2001.0462)
E. Giacobini, Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 18 (2003) S1 (https://doi.org/10.1002/gps.935)
S. Darvesh, Curr. Alzheimer Res. 13 (2016) 1173 (https://doi.org/10.2174/1567205013666160404120542)
Z. Cai, Mol. Med. Rep. 9 (2014) 1533 (https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2014.2040)
S. Manzoor, N. Hoda, Eur. J. Med. Chem. 206 (2020) 112787 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112787)
P. O. Patil, S. B. Bari, S. D. Firke, P. K. Deshmukh, S. T. Donda, D.A. Patil, Bioorg. Med. Chem. 21 (2013) 2434 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2013.02.017)
G. Nesi, S. Sestito, M. Digiacomo, S. Rapposelli, Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 17 (2017) 3062 (https://doi.org/10.2174/1568026617666170607114232)
L. Mucke, Nature 461 (2009) 895 (https://doi.org/10.1038/461895a)
L. Blaikie, P. Kay, P. K. T. Lin, MedChemComm 10 (2019) 2052 (https://doi.org/10.1039/C9MD00337A)
T. Tomašić, L. Peterlin Masic, Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 14 (2014) 130 (https://doi.org/10.2174/1568026613666131113153251)
J. H. Xu, Y. L. Fan, J. Zhou, J. Heterocycl. Chem. 55 (2018) 1854 (https://doi.org/10.1002/jhet.3234)
Chemical Computing Group, M. O. E. Molecular Operating Environment. Chemical Computing Group, Montreal, 2008
BioSolveIT-SeeSAR (https://www.biosolveit.de/SeeSAR).