Deep eutectic solvents formed by pharmaceutical ingredients and their potential influences on solid preparations Scientific paper
Main Article Content
Abstract
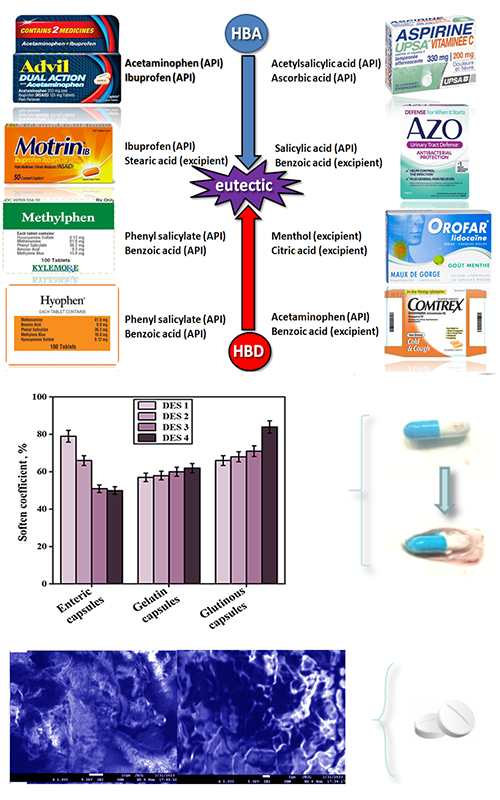
Some active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and excipients can form deep eutectic solvents (DESs), which will lead to severe defects in solid preparations. This work first prepared related typical DESs by mixing APIs and excipients from marketable drugs. Then two different types of the binary eutectic mixtures were investigated, which were composed of menthol (HBD) and citric acid (HBA), ME/CA, as well as phenyl salicylate (HBA) and benzoic acid (HBD), Salol/BA. These binary mixtures were applied to investigate their possible effects on capsules and tablets, which could be liquefaction or the stickiness of the solid formulations. The comprehensive characterizations and studies on phase behaviours of the binary mixtures were carried out, and the spectral analysis confirmed the formation of the eutectic liquids from individual components. Furthermore, the binary mixtures have increased the tablet strength when increasing the compression force, leading to the stickiness of powders during pressing. Moreover, the capsules were softened by the existence of DESs. After morphological observation and quantitative analysis, the corresponding suggestions and countermeasures were provided in the conclusions.
Downloads
Metrics
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution license 4.0 that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
Funding data
-
National Natural Science Foundation of China
Grant numbers 82273814 -
Natural Science Foundation of Sichuan Province
Grant numbers 2022NSFSC1604
References
A. R. C. Duarte, A. S. D. Ferreira, S. Barreiros, E. Cabrita, R. L. Reis, A. Paiva, Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm.114 (2017) 296 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2017.02.003)
B. S. Đorđević, D. Z. Troter, V. B. Veljković, M. L. J. Kijevčanin, I. R. Radović, Z. B. Todorović, J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 85 (2020) 1303 (https://doi.org/10.2298/JSC200425050D)
F. Al-Akayleh, R. M. Khalid, D. Hawash, E. Al-Kaissi, I. S. Al-Adham, N. Al-Muhtaseb, M. Jaber, M. Al-Remawi, P. J. Collier, Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 75 (2022) 607 (https://doi.org/10.1111/lam.13699)
M. Patrycja, P. Andrzej, B. Grzegorz, J. Chromatogr., A 1570 (2018) 28 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2018.07.070)
G. Q. Zhong, R. R. Jia, Y. Q. Jia, Adv. Mater. Res. 549 (2012) 292 (https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.549.292)
M. Phutke, A. R. Raichur, A. K. Suresh, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 61 (2022) 11636 (https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.2c00513)
M. M. Santos, L. C. Branco, Pharmaceut. 12 (2020) 909 (https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12100909)
Y. Liu, Y. Wu, J. Liu, W. Wang, Q. Yang, G. Yang, Int. J. Pharmaceut. 622 (2022) 121811 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2022.121811)
M. H. Zainal-Abidin, M. Hayyan, G. C. Ngoh, W. F. Wong, C. Y. Looi, J. Control. Rel. 316 (2019) 168 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2019.09.019)
A. Gutiérrez, S. Aparicio, M. Atilhan, Phys. Chem. 21 (2019) 10621 (https://doi.org/10.1039/C9CP01408J)
H. Shekaari, M. T. Zafarani-Moattar, M. Mokhtarpour, J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 19 (2022) 4275 (https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-022-02602-y)
Y. Liu, X. Wei, J. Chen, Y. L. Yu, J. H. Wang, H. Qiu, Anal. Chem. 94 (2022) 5970 (https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.2c00428)
S. Chattoraj, P. Daugherity, T. McDermott, A. Olsofsky, W. J. Roth, M. Tobyn, J. Pharm. Sci. 107 (2018) 2267 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xphs.2018.04.029)
D. Setyawan, D. Isadiartuti, S. D. Betari, D. P. Paramita, Indones. J. Pharm.27 (2016) 28 (https://doi.org/10.14499/indonesianjpharm27iss1pp28)
M. Zdanowicz, K. Wilpiszewska, T. Spychaj, Carbohyd. Polym. 200 (2018) 361 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.07.078)
M.H.Shafie, R.Yusof, C.Y.Gan, J. Mol. Liq. 288 (2019) 111081 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.111081)
Q. Zhang, K. D. O. Vigier, S. Royer, F. Jérôme, Chem. Soc. Rev. 41 (2012) 7108 (https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CS35178A)
K. A. Omar, R. Sadeghi, J. Mol. Liq. 360 (2022) 119524 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2022.119524)
U. R. Kapadi, D. G. Hundiwale, N. B. Patil, M. K. Lande, P. R. Patil, Fluid Phase Equilib. 192 (2001) 63 (https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-3812(01)00621-5)
H. Shekaari, M. T. Zafarani-Moattar, M. Mokhtarpour, S. Faraji, J. Mol. Liq. 289 (2019) 111077 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.111077)
M. Bi, S. J. Hwang, K. R. Morris, Thermochim. Acta 404 (2003) 213 (https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-6031(03)00185-0)
S. Swaminathan, B. Ganapathy, M. Wang, F. Wang, J. Wooding, J. Frankel, S. Chiruvolu, S. Rengarajan, P. Narwankar, Powder Technol. 425 (2023) 118525 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2023.118525)
R. N. Dave, L. Beach, M. P.Mullarney, C. Ghoroi, in Proceedings of AIChE Annual Meeting (2010), 2010 Annual Meeting, Food, Pharmaceutical & Bioengineering Division, New York (https://www.aiche.org/conferences/aiche-annual-meeting/2010/proceeding/paper/444f-novel-continuous-device-surface-modification-cohesive-pharmaceutical-powders-dry-coating-nano).