A comparative study on ecological risk assessment of some potentially toxic elements accumulation in surface sediment of stagnant and running water ecosystems in Meriç delta wetland, Turkish Thrace Scientific paper
Main Article Content
Abstract
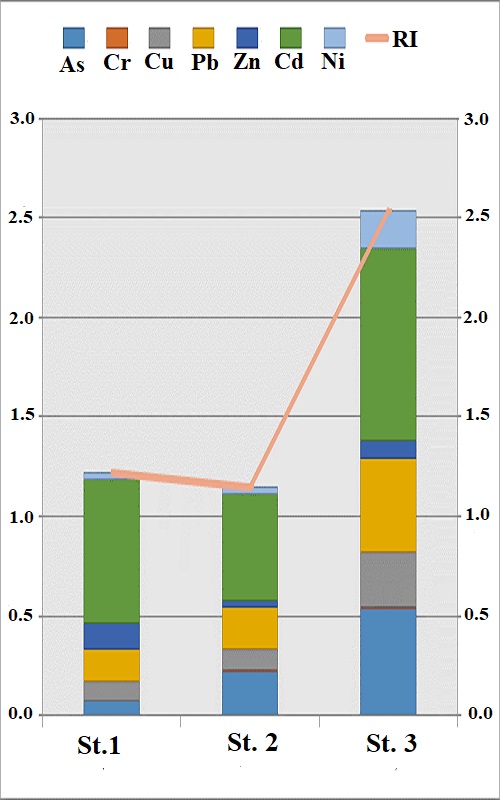
This study determined arsenic, chromium, cadmium, copper, zinc, nickel and lead concentrations in the sediment of the lake and river and evaluated their ecological risk profile and compared the ecological risk profile of some potentially toxic elements accumulated in surface sediment of stagnant and running water ecosystems in the Meriç Delta Wetland, Turkish Thrace which is located in the European part of Turkey and have two important river systems, Meriç and Ergene, which provide freshwater resources for the region. Sediment samples were taken seasonally from three stations (one station from the river and two stations from the lake) in 2020. Ecological and biological risk analyses were calculated using the potential ecological risk index (RI), biological risk index (mERM-Qi), contamination factor (CF), contamination degree (CD) and pollution load index (PLI). As a result, although RI stated that Cd was determined as the riskiest element and mERM-Qi stated that Zn was determined as the riskiest element, indicated that there were no high ecological risks besides the investigated elements in the area. Although it is expected that the sediment quality of running water systems is better than that of stagnant water systems, the results of risk indices in the present study showed that the station selected for running water was the riskiest station in terms of potentially toxic elements.
Downloads
Metrics
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution license 4.0 that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
References
M. S. Islam, R. Proshad, S. Ahmed, Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 24 (2018) 699 (https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2017.1397499)
C. Tokatlı, Environ. Monit. Assess. 191 (2019) 706 (https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7885-2)
G. B. Yu, Y. Liu, S. Yua, S. C. Wuc, A. O. W. Leung, X. S. Luo, B. Xua, H. B. Li, M. H. Wong, Chemosphere 85 (2011) 1080 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.07.039)
C. Tokatlı, Aquat. Sci. Eng. 34 (2019) 90 (https://doi.org/10.26650/ASE2019545919)
F. Ustaoğlu, Md S. Islam, Aqua. Ecol. Indic. 113 (2020) 106237 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.106237)
L. Håkanson, Water Res. 14 (1980) 975 (https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8)
M. Varol, J. Hazard. Mater. 195 (2011) 355 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.08.051)
A. Çiçek, C. Tokatlı, E. Köse, Pak. J. Zool. 45 (2013) 1335 (https://www.zsp.com.pk/pdf45/1335-1341%20_21_%20PJZ-1403-13%2029-8-13%20CHECKED%20manuscript.pdf)
C. Tokatlı, A. Çiçek, E. Köse, Iğdır Univ. J. Inst. Sci. Tech. 7 (2017) 267 (https://www.igdir.edu.tr/Addons/Resmi/announc/5053/5053-article-file14.pdf-abstract-file.pdf)
M. Maanan, M. E. Barjy, N. Hassou, H. Zidane, B. Zourarah, M. Maanan, Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 24 (2018) 602 (https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2017.1394176)
Ş. Fikirdeşici-Ergen, Commun. Fac. Sci. Univ. Ank., C 29 (2020) 202 (https://dergipark.org.tr/en/download/article-file/1148564)
C. Tokatlı, A. Uğurlu, E. Köse, A. Çiçek, N. Arslan, H. Dayıoğlu, Ö. Emiroğlu, Environ. Earth Sci. 80 (2021) 17 (https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-09333-4)
C. Tokatli, F. Ustaoğlu, Environ. Earth Sci. 79 (2020) 426 (https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-09171-4)
O. Akyol, T. Ceyhan, EgeJFAS 27 (2010) 31 (http://www.egejfas.org/tr/download/article-file/57391)
C. Tokatlı, Arch. Environ. Prot. 43 (2017) 34 (https://doi.org/10.1515/aep-2017-0007)
C. Tokatlı, Acta Aliment. 47 (2018) 470 (https://doi.org/10.1556/066.2018.47.4.10)
G. B. Aydın, B. Çamur-Elipek, Oceanol Hydrobiol Stud. 51 (2022) 212 (https://doi.org/10.26881/oandhs-2022.2.09)
USEPA, Method 3051a: Microwave Assisted Acid Dissolution of Sediments, Sludges, Soils, and Oils, Revision 1, United States Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC, 2007 (https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-12/documents/3051a.pdf)
J. T. Creed, C. A. Brockhoff, T. D. Martin, Method 200.8, Determination of Trace Elements in Waters and Wastes by Inductively Coupled Plasma – Mass Spectrometry, 1994 (https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-06/documents/epa-200.8.pdf)
E. R. Long, C. G. Ingersoll, D. D. MacDonald, Environ. Sci. Technol. 40 (2005) 1726 (https://doi.org/10.1021/es058012d)
D. C. Tomlinson, J. G. Wilson, C. R. Harris, D. W. Jeffery, Helgolander Meeresunters 33 (1980) 566 (https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02414780)
N. Köleli, Ç. Kantar, Ekoloji 14 (2005) 55 (https://silo.tips/download/fosfat-kayasy-fosforik-asit-ve-fosforlu-gbrelerdeki-toksik-ayr-metal-cd-pb-ni-as)
Z. Elhaj Baddar, E. Peck, X. Xu, PLOS One 16 (2021) e0255527 (https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0255527)
K. R. Reddy, R. D. Delaune, Biogeochemistry of Wetlands: Science and Applications, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 2008 (https://doi.org/10.1201/9780203491454)
T. O. Genç, F. Yılmaz, J. Adv. Agric. 6 (2016) 804 (https://doi.org/10.24297/jaa.v6i1.5386)
S. Kükrer, A. E. Erginal, Ş. Kılıç, Ö. Bay, T. Akarsu, E. Öztura, Environ. Monit. Assess. 192 (2020) 359 (https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08336-9)
M. Yabanlı, A. Yozukmaz, İ. Şener, H. Hasanhocaoğlu Yapıcı, E. Çetin Kasa, Acta Aquat. Turc. 18 (2022) 109 (https://doi.org/10.22392/actaquatr.993135).