Modelling and optimisation of activated sludge process using artificial neural networks and genetic algorithms
Main Article Content
Abstract
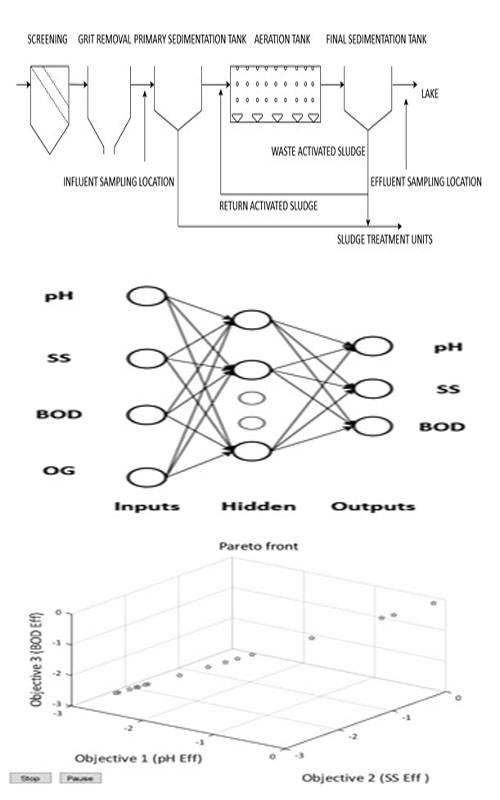
Mathematical modelling of activated sludge process (ASP) is done using multi-layer perceptron neural networks (MLP-ANN) to predict effluent water quality parameters and multi objective genetic algorithm (MOGA) is employed to optimise influent water quality parameters so that the concentration of contaminants in the effluent stream is minimized . The study area selected was in a central district of southern state of India. The effluent parameters to be investigated are pH, suspended solids (SS) and biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) and the influent parameters to be optimised are pH, suspended solids (SS), biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) and oil and grease (O&G). The model is evaluated based on statistical parameters of correlation coefficient R and mean square error (MSE). MATLAB R2019a are used for modelling and optimisation study. It has been found that effluent pH, SS and BOD were predicted with an overall R of 0.9207 and MSE of 0.0091. During optimisation of influent parameters, it was found that optimum values of the decision variables pH Inf lies between 6-8 ,optimum values of SS Inf lies between 68-380 , optimum values of BOD Inf lies between 155-692 and optimum values of O&G Inf lies between 8-45 when the objective functions were minimised simultaneously.
Downloads
Metrics
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution license 4.0 that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
References
T. Y. Pai, P. Y. Yang, S. C. Wang, M. H. Lo, C. F. Chiang, J. L. Kuo, H. H. Chu, H. C. Su, L. F. Yu, H. C. Hu, Y. H. Chang, Appl. Math. Model. 35 (2011) 3674–3684 (https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2011.01.019)
V. V. Nair, H. Dhar, S. Kumar, A. K. Thalla, S. Mukherjee, J. W. C. Wong, Bioresour. Technol. 217 (2016) 90–99 (https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.03.046)
V. Pareek, M. P. Brungs, A. Adesina, R. Sharma, J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 149 (2002) 139–146 (https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1010-6030(01)00640-2)
N. J. De Vos, T. H. M. Rientjes, Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 9 (2005) 111–126 (https://dx.doi.org/10.5194/HESS-9-111-2005)
M. M. Hamed, M. G. Khalafallah, E. A. Hassanien, Env. Model. Softw. 19 (2004) 919–928 (https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2003.10.005)
M. S. Nasr, M. A. E. Moustafa, H. A. E. Seif, G. El Kobrosy, Alexandria Eng. J. 51 (2012) 37–43 (https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2012.07.005)
M. Hamada, H. A. Zaqoot, A. A. Jreiban, J. Appl. Res. Water Wastewater 9 (2018) 399–406 (https://dx.doi.org/10.22126/arww.2018.874)
M. Arbib, M. Bota, Neural Networks 16 (2003) 1237–1260 (https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2003.08.002)
D. Howard, B. Mark, Neural Network Toolbox User’s Guide, 2004.
N. Srinivas, K. Deb, Evol. Comput. 2 (1994) 221–248 (https://dx.doi.org/10.1162/evco.1994.2.3.221)
IS 3025-1: Methods of sampling and test (physical and chemical) for water and wastewater Part 1 (1987)
R. Rustum, Modelling Activated Sludge Wastewater Treatment Plants Using Artificial Intelligence Techniques (Fuzzy Logic and Neural Networks), Heriot-Watt University School, 2009.
K. Hornik, M. Stinchcombe, H. White, Neural Networks 2 (1989) 359–366 (https://doi.org/10.1016/0893-6080(89)90020-8)
F. S. Mjalli, S. Al-Asheh, H. E. Alfadala, J. Env. Manage. 83 (2007) 329–338 (https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2006.03.004)
S. Haykin, Neural Network-A Comprehensive Foundation, Second ed., Pearson Education, New Delhi, 1999.
N. Kaur, Modeling and multi-objective optimization of wastewater treatment process, University of Western Ontario, Electronic Thesis and Dissertation Repository (2023) 9146 (https://ir.lib.uwo.ca/etd/9146)
Ö. Yeniay, Math. Comput. Appl. 10 (2005) 45–56 (https://dx.doi.org/10.3390/mca10010045).