3D-QSAR study of adenosine 5'-phosphosulfate (APS) analouges as ligands for APS reductase Scientific paper
Main Article Content
Abstract
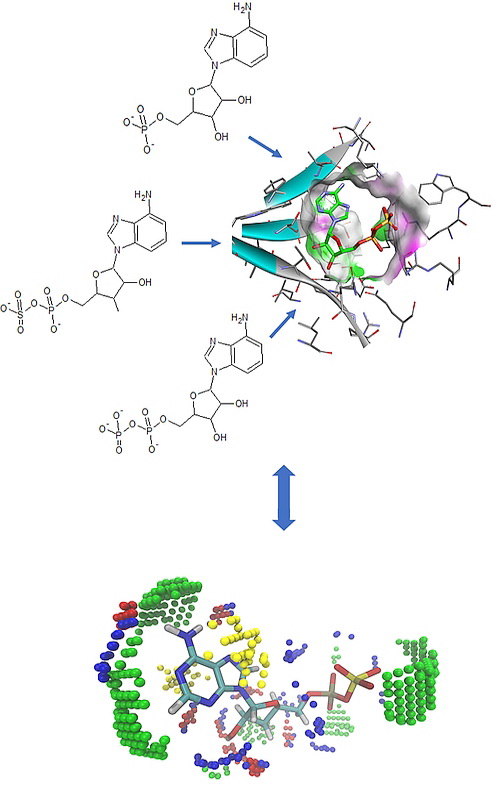
Metabolism of sulfur (sulfur assimilation pathway, SAP) is one of the key pathways for the pathogenesis and survival of persistant bacteria, such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb), in the latent period. Adenosine 5'-phosphosulfate reductase (APSR) is an important enzyme involved in the SAP, absent from the human body, so it might represent a valid target for development of new antituberculosis drugs. This work aimed to develop 3D-QSAR model based on the crystal structure of APSR from Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which shows high degree of homology with APSR from Mtb, in complex with its substrate, adenosine 5'-phosphosulfate (APS). 3D-QSAR model was built from a set of 16 nucleotide analogues of APS using alignment-independent descriptors derived from molecular interaction fields (MIF). The model improves the understanding of the key characteristics of molecules necessary for the interaction with target, and enables the rational design of novel small molecule inhibitors of Mtb APSR.
Downloads
Metrics
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.

Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution license 4.0 that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
References
REFERENCES
R. Schnell, G. Schneider, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 396 (2010) 33 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.02.118)
O. Poyraz, K. Brunner, B. Lohkamp, H. Axelsson, L. G. J. Hammarström, R. Schnell, G. Schneider, PLOS ONE 10 (2015) e0121494 (https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0127016)
R. Iwanicka-Nowicka, A. Zielak, A. M. Cook, M. S. Thomas, M. M. Hryniewicz, J. Bacteriol. 189 (2007) 1675 (https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.00592-06)
P. B. Palde, A. Bhaskar, L. E. Pedro Rosa, F. Madoux, P. Chase, V. Gupta, T. Spicer, L. Scampavia, A. Singh, K. S. Carroll, ACS Chem. Biol. 11 (2015) 172 (https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.5b00517)
J. A. Hong, D. P. Bhave, K. S. Carroll, J. Med. Chem. 52 (2009) 5485 (https://doi.org/10.1021/jm900728u)
S. K. Hatzios, C. R. Bertozzi, PLOS Pathog 7 (2011) e1002036 (https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1002036)
S. Cosconati, J. A. Hong, E. Novellino, K. S. Carroll, D. S. Goodsell, A. J. Olson, J. Med. Chem. 51 (2008) 6627 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2011.08.021)
H. Wieman, K. Tøndel, E. Anderssen, F. Drabløs, Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 4 (2004) 79 (https://doi.org/10.2174/1389557043403639)
OMEGA 2.5.1.4: OpenEye Scientific Software, Santa Fe, NM (http://www.eyesopen.com)
P. C. D. Hawkins, A. G. Skillman, G. L. Warren, B. A. Ellingson, M. T. Stahl, J. Chem. Inf. Model. 50 (2010) 572 (https://doi.org/10.1021/ci100031x)
ROCS 3.2.1.4: OpenEye Scientific Software, Santa Fe, NM (http://www.eyesopen.com)
P. C. D. Hawkins, A. G. Skillman, A. Nicholls, J. Med. Chem. 50 (2007) 74 (https://doi.org/10.1021/jm0603365)
M. Pastor, G. Cruciani, I. McLay, S. Pickett, S. Clementi, J. Med. Chem. 43 (2000) 3233 (https://doi.org/10.1021/jm000941m)
J. Chartron, K. S. Carroll , C. Shiau, H. Gao, J. A. Leary, C. R. Bertozzi, C. David Stout C. J. Mol. Biol. 364 (2006) 152 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2011.08.021).