Mass transfer in inverse fluidized beds Scientific paper
Main Article Content
Abstract
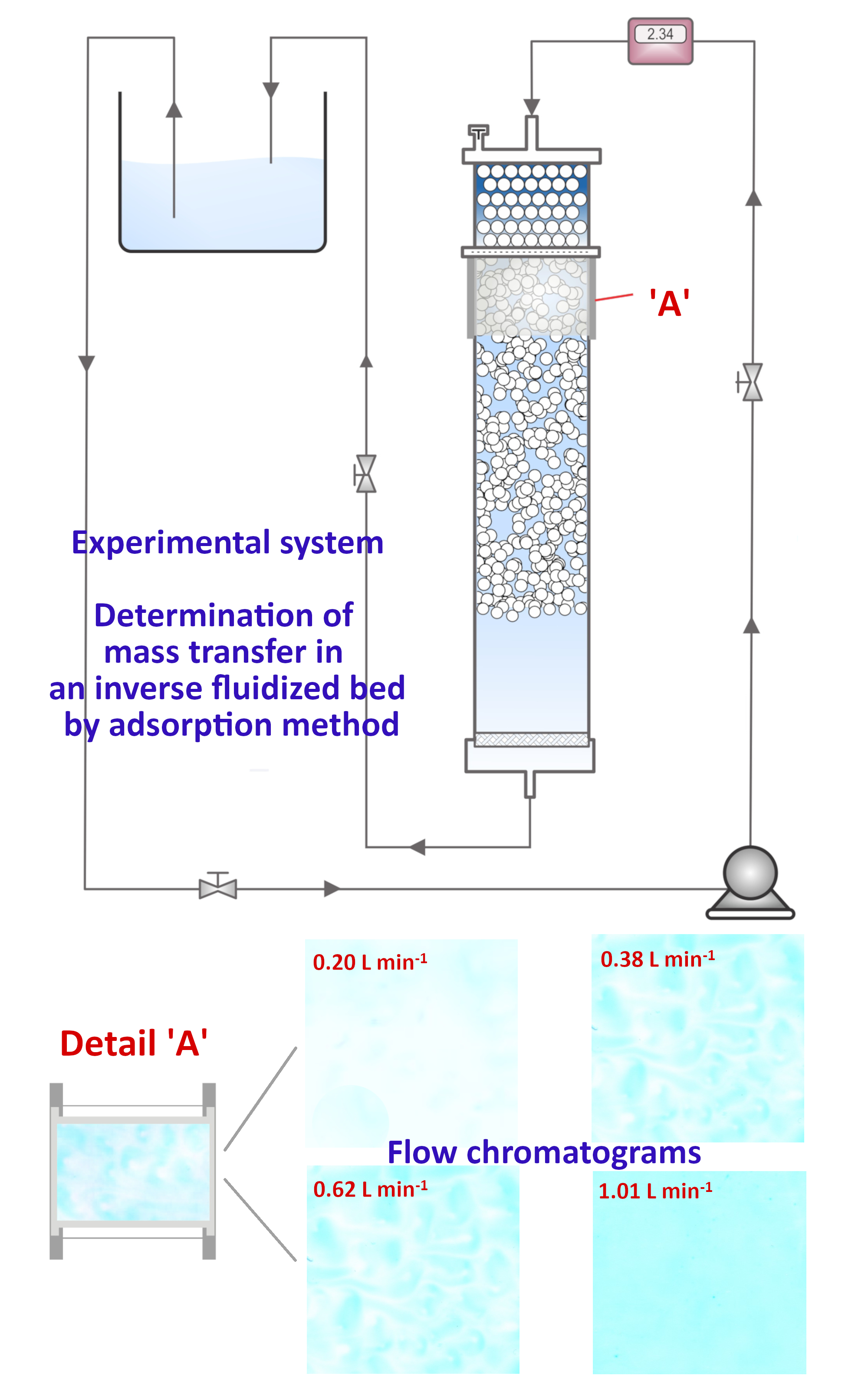
In this work, the coefficient of fluid-wall mass transfer in an inverse fluidized bed was determined using the adsorption method. The experiments were carried out in a column with a diameter of 45 mm with spherical and non-spherical particles of polypropylene and polyethylene with a diameter of 3.3–4.9 mm and a density of about 930 kg m-3. A diluted solution of methylene blue was used as a fluidization medium, which was adsorbed on part of the surface of the column on silica gel. The obtained results showed that the presence of particles during inverse fluidization does not contribute significantly to mass transfer compared to the influence of particles on transfer in conventional fluidized beds. Therefore, the pseudo-fluid concept was introduced into the analysis and an empirical correlation was performed to determine the mass transfer coefficient. The obtained results were compared with literature correlations for inverse and conventional fluidized beds.
Downloads
Metrics
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.

Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution license 4.0 that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
Funding data
-
Ministarstvo Prosvete, Nauke i Tehnološkog Razvoja
Grant numbers 451-03-47/2023- 01/200135;451-03-47/2023-01/200026
References
D. Wang, T. Silbaugh, R. Pfeffer Y. S. Lin, Powder Technol. 203 (2010) 298 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2010.05.021)
S. S. Begum, K. V. Radha, Korean J. Chem. Eng. 31 (2014) 436 (https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-013-0260-z)
W. Sokol, A. Ambaw, B. Woldeyes, Chem. Eng. J. 150 (2009) 63 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2008.12.021)
M. Rajasimman, C.Karthikeyan, Int. J. Environ Res. 3 (2009) 569 (https://doi.org/10.22059/IJER.2010.72)
D.G. Karamanev, L.N. Nikolov, Environ. Prog. 15 (1996) 3 (https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.670150319)
I.Nikov, D. Karamanev, AIChe J. 37 (1991) 781 (https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.690370515)
K.A. Kumar, G.V.S. Sarma, M. Vijay, K.V. Ramesh, Test Eng. Manage. 83 (2020) 14318 (http://www.testmagzine.biz/index.php/testmagzine/article/view/9657/7397)
S. Končar-Durđević, Nature 172, 878 (1953) 858 (https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036024409090246)
D. Jaćimovski, PhD Thesis, Faculty of Technology and Metallurgy, Belgrade, 2017 (http://phaidrabg.bg.ac.rs/o:17299)
N. Bošković-Vragolović, R. Garić-Grulović, Ž.Grbavčić, R.Pjanović, Russ. J. Phys. Chem. 83 (2009) 1550 (https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036024409090246)
SigmaScan Software, Jandel Scientific, Erkrath, 1999
M. Đuriš, T. Kaluđerović Radoičić, R. Garić-Grulović, Z. Arsenijević, Ž. Grbavčić, Powder Technol. 246 (2013) 98 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2013.05.009)
D.Jaćimovski, R.Garić-Grulović, N.Vučetić, R. Pjanović, N. Bošković-Vragolović, Powder Technol. 303 (2016) 68 (https://doi.org/10.1016/J.powtec.2016.09.025)
Ž.Grbavčić, Z. Arsenijević, R.Garić-Grulović, Powder Technol. 190 (2009) 283 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2008.08.005)
R. Garić-Grulović, Ž. Grbavčić, Z. Arsenijević, J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 70 (2005) 775 (http://dx.doi.org/10.2298/JSC0505775G)
N. Yutani, N. Ototake , L.T. Fan, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 26 (1987) 343 (https://doi.org/10.1021/ie00062a028)
S. Marooka, K. Kusakabe, Y. Kato, Int. Chem. Eng. 20 (1980) 433
D. Kunii, O. Levenspiel, Fluidisation Engineering, Wiley, New York, 1969, p. 195.