Potentially toxic elements from different environmental compartments of the River Watershed in Eastern Serbia – Assessment of the human health risk Scientific paper
Main Article Content
Abstract
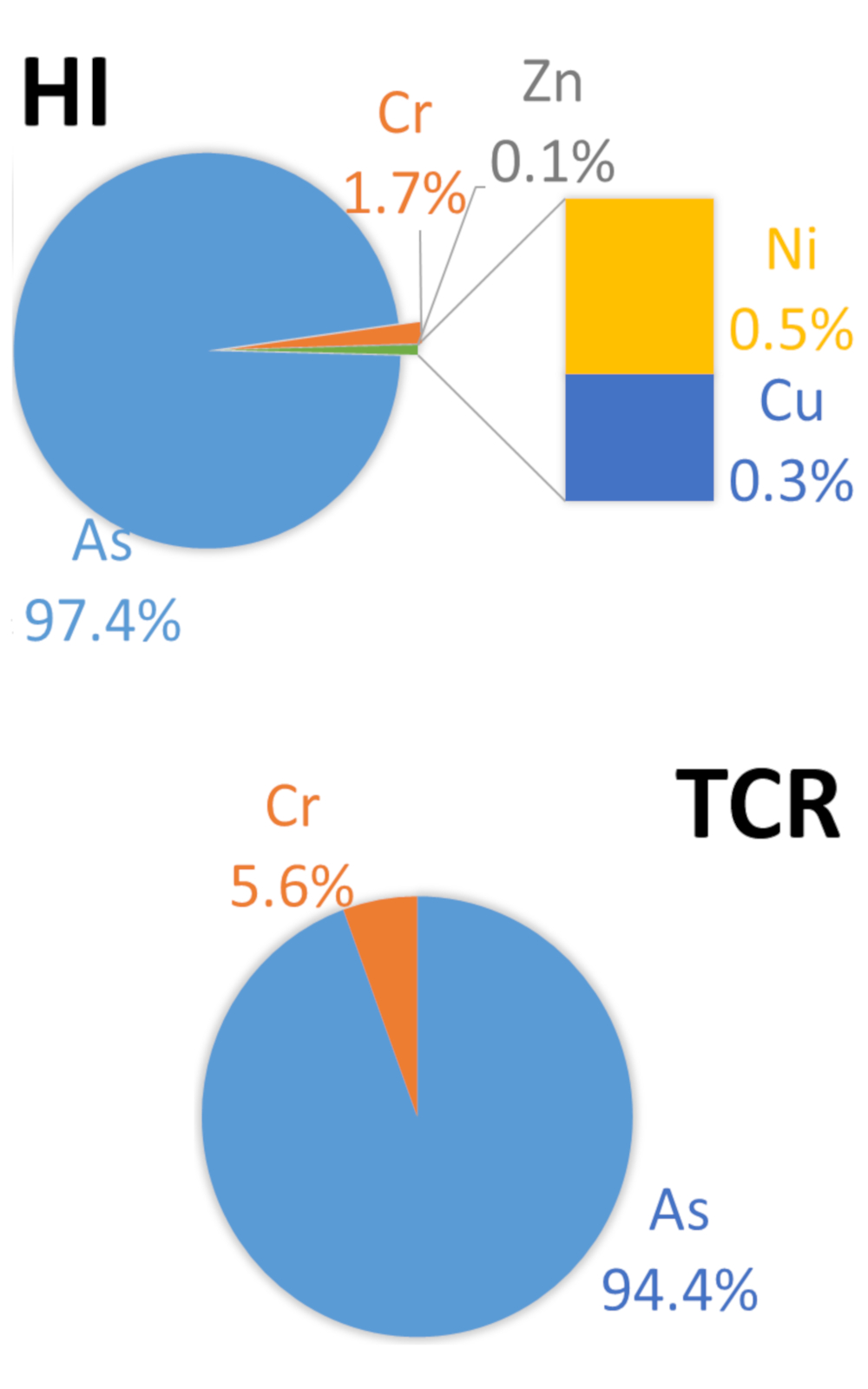
This study assessed human health risks due to exposure to potentially toxic elements (PTES) in soil and river water in eastern Serbia. Concentrations of As, Cu, Cd, Zn, Pb, Ni and Cr were measured in soil and river water from the Vlasina watershed area. The concentrations of Cl-, SO42- and NO3- were also measured in the river water. According to the Regulation of the Republic of Serbia, the water quality of the investigated rivers corresponds to the surface water quality Class I and II. The content of PTEs in soil was below soil guideline values. Children were more sensitive than adults when exposed to PTE in water and soil. Arsenic was the dominant contributor to the total non-carcinogenic and carcinogenic risks for exposure to PTE in water. For PTE in soil, As had the dominant contribution to non-carcinogenic risks, and Ni to carcinogenic risks. All hazard index (HI) values for adults and children are less than 1, which indicates that the impact of PTEs in the examined river water and soil on human health is insignificant. Ingestion route is a major contributor to both total non-carcinogenic and carcinogenic risks.
Downloads
Metrics
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution license 4.0 that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
Funding data
-
Ministarstvo Prosvete, Nauke i Tehnološkog Razvoja
Grant numbers Contract No: 451-03-66/2024-03/200026
References
Ö. Canpolat, M. Varol, Ö. Ö. Okan, K. K. Eriş, M. Çağlar, Environ. Res. 190 (2020) 110012 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.110012
S. M. Shaheen, V. Antoniadis, E. Kwon, H. Song, S-L. Wang, Z-Y. Hseu, J. Rinklebe, Environ. Poll. 262 (2020) 114312 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114312)
M. S. Islam, Environ. Earth Sci. 28 (2021) 2987 (https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12541-5)
C. Tokatli, F. Ustaoglu., Environ. Earth Sci. 79 (2020), 426 (https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-09171-4)
C. Tokatli, Environ. Earth Sci. 80 (2021) 156 (https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09467-z)
U.S. EPA, Risk assessment guidance for Superfund. Volume I: Human Health Evaluation Manual (Part A). Interim Final. Office of Emergency and Remedial Response. EPA/540/1‐89/002, 1989
E. de Andrade Passos, J. C. Alves, I. S. dos Santos, J. P. H Alves, C. A. B. Garcia, C. S. Costa, Microchem. J. 96 (2010) 50 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2010.01.018)
R.A. Sutherland, Anal. Chim. Acta 680 (2010) 10 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2010.09.016)
S. Sakan, A. Popović, I. Anđelković, D. Đorđević, Environ. Geochem. Health 38 (2016) 855 (https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-015-9766-0)
A. Facchinelli, E. Sacchi, L. Mallen, Environ. Pollut. 14 (2001) 313 (https://doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(00)00243-8)
S. Sakan, I. Gržetic, D. Ðorđević, Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 14 (2007) 229 (https://doi.org/10.1065/espr2006.05.304)
U.S.EPA, Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund Volume I: Human Health Evaluation Manual (Part E, Supplemental Guidance for Dermal Risk Assessment) Final. OSWER 9285.7-02EP, 2004
U.S.EPA, Exposure Factors Handbook 2011 Edition (Final Report). U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC, EPA/600/R-09/052F, 2011
U.S.EPA, 2024. Regional Screening Level (RSL) Summary Table (TR=1E-06 THQ=1.0), https://semspub.epa.gov/work/HQ/404463.pdf (accessed 12 October 2024)
Miladinović, B., Đokanović, S., Pirotski zbornik 44 (2019) 147 (https://nbpi.org.rs/wordpress/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/Pirotski-zbornik-44.pdf) (in Serbian)
S. Sakan, A. Mihajlidi-Zelic, S. Frančišković-Bilinski, D. Đordević, Front. Environ. Sci. 10 (2022) 909858 (https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2022.909858)
L. Li Vigni, K. Daskalopoulou, S. Calabrese, L. Brusca, S. Bellomo, C. Cardellini, K. Kyriakopoulos, F. Brugnone, F. Parello, W. D’Alessandro, Sci. Rep. 13 (2023) 11191 (https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-38349-6)
Regulation on limit values of pollutants in surface and ground waters and sediment and deadlines for their achievement, Off. Gaz. Rep. Serbia 50 (2012) (in Serbian)
Council of the European Communities (CEC), The protection of the environment, and in particular of the soil, when sewage sludge is used in agriculture. Council Directive of 12 june 1986, Off. J. Eur. Communities 181, Issue 6 (1986)
Government of Western Australia, Аssessment levels for Soil, Sediment and Water, Department of Environment and Conservation, 2010
M. Antonijević Nikolić, J. Đuričić Milanković, Đ. Nikolić, Zaštita Materijala 62 (2021) 83. (https://doi.org/10.5937/zasmat2102083A) (in Serbian)
I. Gržetić, R. H. A. Ghariani, J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 73 (2008) 923 (https://doi.org/10.2298/JSC0809923G)
C. Reimann, K. Fabian, M. Birke, P. Filmozer, A. Demetriades, P. Negrél, K. Oorts, J. Matschullat, P. Caritat, Appl. Geochem. 88 (2018) 302 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2017.01.021)
M. Poznanović Spahić, D. Manojlović, P. Tančić, Ž. Cvetković, Z. Nikić, R. Kovačević, S. Sakan, Environ. Monit. Assess. 191 (2019) 133 (https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7268-8)
L. Li, J. Wu, J. Lu, K. Li, X. Zhang, X. Min, C. Gao, J. Xu, Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 241 (2022) 113775 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113775)
S. S. Alarifi, A. S. El-Sorogy, K. Al-Kahtany, S. A. Hazaea, J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 35 (2023) 102826 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2023.102826).