Apoptosis induction in HeLa cervical cancer cell line by steroidal 16,17-seco-16,17a-dinitriles Scientific paper
Main Article Content
Abstract
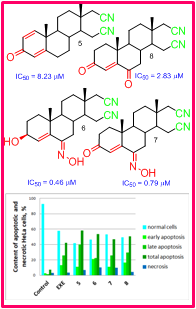
Steroids are good candidates for drug development, thanks to their low general toxicity and possibility for structure modifications connected with change of their activity. Several 16,17-secoandrost-4-ene-16,17a-dinitrile compounds were synthesized and screened for anticancer effect previously, including 6-oxo and 6-hydroxyimino compounds. This research is continued with the attempts for different synthetic strategy and evaluation of anticancer effect mechanism. Synthesis of 3-hydroxyimino compounds was successful, but inseparable mix of isomers was excluded from biological tests. Tested secodinitriles expressed cytotoxic effect on HeLa cervix cancer cells as a model system, with submicromolar to molar IC50 values, where 6-substituted derivatives were more effective. After 72 h treatment with equitoxic concentrations equal IC50 values of test compounds the mechanism of this effect was studied using flow cytometry and specific fluorescent dyes. Modest change in both G0/G1 and G2/M resting phases and change in mitochondrial membrane potential were noticed, while the most pronounced effect was apoptosis induction. Total apoptosis was in range 50.72–58.31 % in all cell samples treated with secodinitriles, compared to 7.44 % in control samples. Total percent of dead cells, including both apoptotic and necrotic, ranged from 55.24 to 65.34 %, compared to 10.68 % in control. Selectivity towards cancer cells is very important feature of these compounds indicating their potential use as lead compounds in the drug development for the treatment of cancers of steroid hormone-dependent tissues.
Downloads
Metrics
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.

Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution license 4.0 that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
Funding data
-
Ministarstvo Prosvete, Nauke i Tehnološkog Razvoja
Grant numbers 451-03-68/2022-14/200125
References
F. Bray, J. Ferlay, I. Soerjomataram, R. L. Siegel, L. A. Torre, A. Jemal, Cancer J. Clin. 68 (2018) 1 (https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21492)
S. W. Lowe, A. W. Lin, Carcinogenesis 21 (2000) 485 (https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/21.3.485)
J. J. Xu, W. W. Mao, J. Cancer Ther. 7 (2016) 762 (http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jct.2016.710077)
A. Gupta, B. S. Kumar, A. S. Negi, Mol. Biol. 137 (2013) 242 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsbmb.2013.05.011)
J. A. R. Salvador, J. F. S. Carvalho, M. A. C. Neves, S. M. Silvestre, A. J. Leitão, M. M. C. Silva, M. L. Sá e Melo, Nat. Prod. Rep. 30 (2013) 324 (https://doi.org/10.1039/C2NP20082A)
É. Frank, G. Schneider, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 137 (2013) 301 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsbmb.2013.02.018)
R. Jaime, N. Lucia, P. Solange, J. Carlos, Tetrahedron Lett. 38 (1997) 1833 (https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-4039(97)00163-9)
J. Cui, L. Huang, L. Fan, A. Zhou, Steroids 73 (2008) 252 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.steroids.2007.10.007)
V. Richmond, V. P. Careaga, P Sacca, J. C. Calvo, M. S. Maier, Steroids 84 (2014) 7 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.steroids.2014.03.001)
J. Poza, M. Rega, V. Paz, B. Alonso, J. Rodriguez, N. Salvador, A. Fernandez, C. Jimenez, Bioorg.Med. Chem. 15 (2007) 4722 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2007.05.003)
N. M. Krstić, M. S. Bjelaković, M. M. Dabović, LJ. B. Lorenc, V. D. Pavlović, J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 69 (2004) 413
A. R. Nikolić, I. Z. Kuzminac, S. S. Jovanović-Šanta, D. S. Jakimov, L. D. Aleksić, M. N. Sakač, Steroids 135 (2018) 101 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.steroids.2018.03.009)
A. R. Nikolić, E. T. Petri, O. R. Klisurić, A. S. Ćelić, D. S. Jakimov, E. A. Djurendić, K. M. Penov Gaši, M. N. Sakač, Bioorg. Med. Chem. 23 (2015) 703 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2014.12.069)
H. J. Phillips, in Tissue Culture, Methods and Applications, P. F. Kruse, M. K. Patterson, Eds., Academic Press, New York, 1973, p. 406 (https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-427150-0.50101-7)
T. Mosmann, J. Immunol. Methods 65 (1983) 55
S. S. Jovanović-Šanta, S. Andrić, N. Andrić, G. Bogdanović, J. A. Petrović, Med. Chem. Res. 20 (2011) 1102 (http://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-010-9442-y)
S. Dasari, P.B. Tchounwou, Eur. J. Pharmacol. 740 (2014) 364 (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4146684/)
E.J. Park, H.K. Kwon, Y.M. Choi, H.J. Shin, S. Choi, PLoS One 7 (2012) 44990 (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23028726)
A. Robinson, Therap. Clin. Risk Managed 5 (2009) 91
D. S. Jakimov, V. V. Kojić, L. D. Aleksić, G. M. Bogdanović, J. J. Ajduković, E. A. Djurendić, K. M. Penov Gaši, M. N. Sakač, S. S. Jovanović-Šanta, Bioorg. Med. Chem. 23 (2015) 7189 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2015.10.015)
BD CellQuest Pro Software, Becton, Dickinson and Company: San Hose, CA,2002
I. Vermes, C. Haanen, H. Steffens-Nakken, C. Reutelingsperger, J. Immunol. Methods 184 (1995) 39 (https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1759(95)00072-I)
M. Yan, P. Zhu, H. M. Liu, H. T. Zhang L. Liu, World J. Gastroenterol. 13 (2007) 2352 (https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i16.2352)
F. F. Fleming, L. Yao, P. C. Ravikumar, L. Funk, B. C. Shook, J. Med. Chem. 53 (2010) 7902 ( https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/jm100762r)
Protein–Ligand Interactions and Drug Design, Methods in Molecular Biology, F. Ballante, Ed., Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, Springer Nature, Vol. 2266, Humana, New York, 2021 (https://link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-1-0716-1209-5)
I. R. Indran, G. Tufo, S. Pervaiz, C. Brenner, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1807 (2011) 735 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2011.03.010).